Abstract
Introduction: molar incisor hypomineralization is a systemic developmental defect that affects one or more permanent first
molars, is frequently associated with permanent incisors, of multifactorial etiology and with various treatment options.
Objective: the case of a patient who presents molar incisor hypomineralization in his first permanent molars with a history of having
suffered from distal renal tubular acidosis is presented, this entity can cause enamel defects
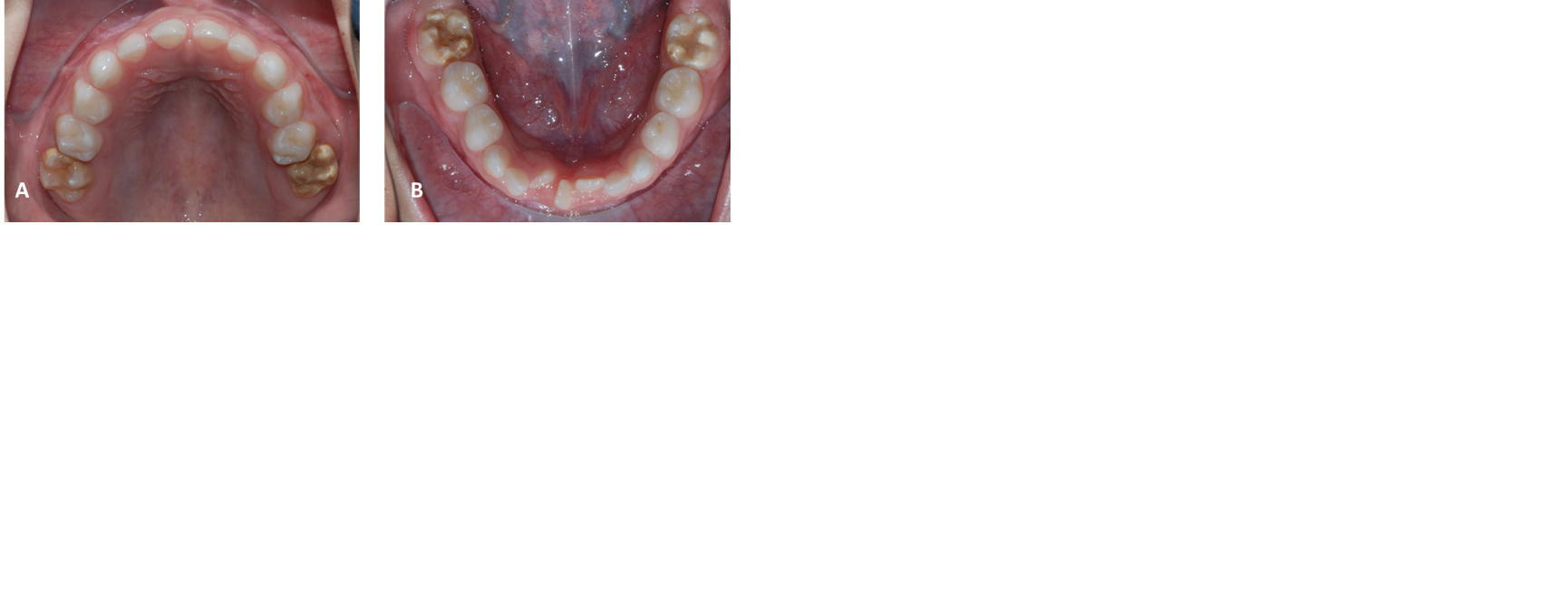
Case report: 7-year-old male diagnosed with distal tubular acidosis at 4 months of age, at the time of the consultation he
had already passed. In his first permanent molars, lesions suggestive of molar incisor hypomineralization were observed. It is
evaluated clinically and radiographically. Glass ionomer restorations were performed, reviewed at six-monthly controls, and at 10
years it was decided to place composite resins on the affected molars. Periodic controls are indicated, which he regularly attends for
14 years.
Conclusion: early identification of molar incisor hypomineralization will allow the application of preventive measures to ensure the permanence of affected teeth in the mouth. It is important to strengthen hygienic practices, especially on affected surfaces, concomitantly with the application of restorative materials.
References
Wright JT, Carrion IA, Morris C. The molecular basis of hereditary enamel defects in humans. J Dent Res. 2015;94(1):52–61.
Lopes LB, Machado V, Mascarenhas P, Mendes JJ, Botelho J. The prevalence of molar-incisor hypomineralization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22405. doi:10.1038/ s41598-021-01541-7
Bandeira Lopes L, Machado V, Botelho J, Haubek D. Molar-incisor hypomineralization: an umbrella review. Acta Odontol Scand. 2021;79(5):359-69. doi:10.1080/00016357.2020.1863461
Elhennawy K, Manton DJ, Crombie F, Zaslansky P, Radlanski RJ, Jost-Brinkmann PG, Schwendicke F. Structural, mechanical and chemical evaluation of molar-incisor hypomineralizationaffected enamel: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol. 2017; 83: 272–81
Almulhim B. Molar and Incisor Hypomineralization. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2021;59(235):295-302. doi:10.31729/jnma.6343.
Rao MH, Aluru SC, Jayam C, Bandlapalli A, Patel N. Molar Incisor Hypomineralization. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016;17(7):609-13.
Padavala S, Sukumaran G. Molar Incisor Hypomineralization and Its Prevalence. Contemp Clin Dent. 2018;9(Suppl 2):S246-S250. doi:10.4103/ccd.ccd_161_18
Silva MJ, Scurrah KJ, Craig JM, Manton DJ, Kilpatrick N. Etiology of molar incisor hypomineralization - A systematic review. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2016;44(4):342-353. doi:10.1111/ cdoe.12229
Sundfeld D, da Silva L, Kluppel OJ, Santin GC de Oliveira RC, Pacheco RR, Pini NI. Molar Incisor Hypomineralization: Etiology, Clinical Aspects, and a Restorative Treatment Case Report. Oper Dent. 2020;45(4):343-51. doi:10.2341/19-138-T
Garot E, Rouas P, Somani C, Taylor GD, Wong F, Lygidakis NA. An update of the aetiological factors involved in molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022 Feb;23(1):23-38.
Bagattoni S, Carli E, Gatto MR, Gasperoni I, Piana G, Lardani L. Predisposing factors involved in the aetiology of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization: a case-control study. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2022;23(2):116-20. doi:10.23804/ejpd.2022.23.02.13.
Lacruz RS, Habelitz S, Wright JT, Paine ML. Dental Enamel Formation and Implications for Oral Health and Disease. Physiol Rev. 2017; 97(3): 939–993. doi:10.1152/physrev.00030.2016
Ferreira SB, de Aquino SN, Pereira PC, Simões e Silva AC, Martelli-Júnior H. Dental findings in Brazilian patients with Fanconi syndrome. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2016;26(1):77-80. doi:10.1111/ipd.12183
Costa SA, Souza SF, Nunes AM. Oral manifestations of renal tubular acidosis associated with secondary rickets: case report. J Bras Nefrol. 2019;41(3):433-5. doi:10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2018-0105
Gómez-Conde S, García-Castaño A, Aguirre M, Herrero M, Gondra L, Castaño L, Madariaga, L. Acidosis tubular renal distal hereditaria: correlación genotípica, evolución a largo plazo y nuevas perspectivas terapéuticas. Nefrología. 2021;41(4):383-90
Misgar RA, Hassan Z, Wani AI, Bashir MI. Amelogenesis imperfecta with distal renal tubular acidosis: a novel syndrome? Indian J Nephrol. 2017;27(3):225–7.
Ravi P, Ekambaranath TS, Arasi SE, Fernando E. 2013. Distal renal tubular acidosis and amelogenesis imperfecta: a rare association. Indian J Nephrol. 23(6):452–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google S]
Dourado DG, Lima CCB, Silva RNC, Tajra FS, Moura MS, Lopes TSP, De Deus Moura LF, de Lima MD. Molar-incisor hypomineralization in quilombola children and adolescents: A study of prevalence and associated factors. J Public Health Dent. 2021;81(3):178-187. doi:10.1111/jphd.12429
Corral C, Rodríguez H, Cabello R, Bersezio C, Cordeiro R, et al. Impacto de la hipomineralización incisivo molar en la experiencia de caries en escolares de 6-12 años en Santiago, Chile. Rev Clin Periodoncia Implantol Rehabil Oral. 2016;9(3):277-283. doi: 10.1016/j.piro.2016.10.003
Buchgraber B, Kqiku L, Ebeleseder KA. Molar incisor hypomineralization: proportion and severity in primary public school children in Graz, Austria. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(2):757-62. doi:10.1007/s00784-017-2150-y
Martignon S, Bartlett D, Manton DJ, Martinez-Mier EA, Splieth C, Avila V. Epidemiology of Erosive Tooth Wear, Dental Fluorosis and Molar Incisor Hypomineralization in the American Continent. Caries Res. 2021;55(1):1-11. doi:10.1159/000512483
Lygidakis NA, Garot E, Somani C, Taylor GD, Rouas P, Wong FSL. Best clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar-incisor-hypomineralization (MIH): an updated. European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022;23(1):3-21. doi:10.1007/s40368-021.
Romo-Pérez C, Lobo-Cortés L, Morales-Rojas MJ, San Martín-López AL, Ramírez-Vera KG. Efecto de la hipomineralización incisivo molar en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud bucal de niños y adolescentes: una revisión sistemática. Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2022;10(4): e130. doi:
21142/2523-2754-1004-2022-130

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.